Do you want to convert your website to app? You might have come across the idea of creating web apps. However, you are not the first, already, millions of mobile applications are available for download.

Smartphones have changed the world forever, whether for good or for bad. Information is accessed at the touch of a screen, and everything you need to know about a brand is just a few clicks away. As more than half of all visits to websites in 2021 will come from mobile devices, consumers don’t need a desktop computer to explore your website.
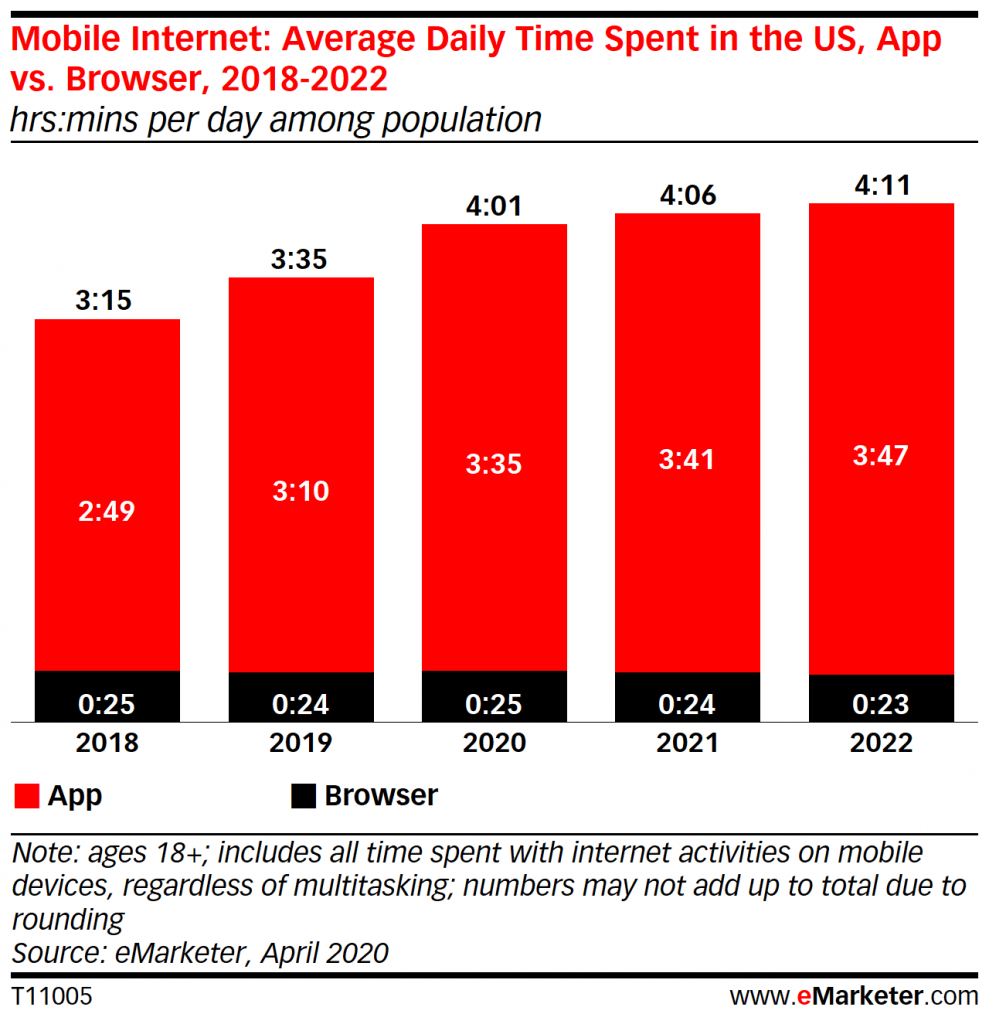
US adults on an average spend at least 4 hours on their mobile devices according to eMarketer.
As per Statista, by 2025 revenue from mobile apps is projected to reach 613 billion U.S. dollars.
Considering the statistics, if you decide to convert a website into an app, you have reached the right place.
To give your customers a mobile-optimized experience, you can convert your website to app (Android or iOS app). The app option is especially useful if your website isn’t the most mobile-friendly on phones or tablets.
In this post, we’ll discuss:
- What is Web application (Web app)
- How Web apps work
- Benefits of Web Apps
- Web Application vs. other application types
Learn More Swing2App Website to app convertor.
What is Web application (Web app)?
The Web application (Web app) is a program that is stored on a remote server and accessed via the Internet through a browser interface. Any component of a web page that performs some function for the user qualifies as a Web app according to Web.AppStorm editor Jarel Remick.
A web application can be used by organizations as well as individuals for numerous reasons and can be designed for a variety of purposes. Webmail, online calculators, and e-commerce shops are common Web applications. Google Sheets, Quora, and Evernote are some of the most popular web apps.
Checkout our Swing2App free website to app creator:
From ordering takeout to planning vacations, web applications may be used for a variety of tasks. A web app might be anything as basic as a contact survey form on a website or an online calculator. Most Web apps can be accessed with any browser; however, some are only accessible through one specific browser.
Web applications are extremely adaptable, allowing users to execute a wide range of tasks. Consumers can use websites to place orders, create a Wishlist, and inquire about items or services, among other things. Employees may also use apps to exchange papers, interact with one another, modify files, and work on projects together. This is especially significant in the current era of remote working.
How Web apps work
Web applications don’t have to be downloaded because they are accessed through the internet. A web browser such as Chrome, Firefox, or Safari can be used to access a Web application.
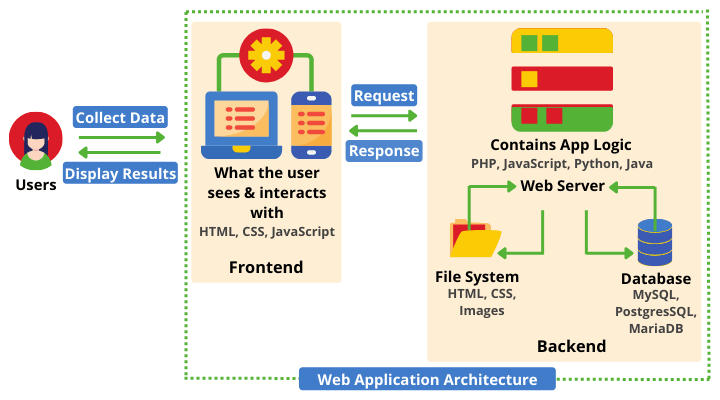
But how web apps work? What are the technical aspects?
The following is a common web application workflow:
- A user sends a request to the server via the internet, either through a web browser or through an app’s user interface.
- The web server sends the request to the appropriate web application server.
- After that, the web application server completes the required job (for example, processing new data) and returns the relevant results.
- The results are then transferred from the web application server to the webserver, along with the required information.
- The web server then replies to the client, displaying the requested information to the user.
Web apps may be created by small teams of developers since they have quick development cycles. JavaScript, HTML5, and Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) are used to create most Web applications. These languages are commonly used in client-side programming to assist develop an application’s front-end. To construct the scripts that a Web app will employ, server-side programming is used. In server-side programming, languages like Python, Java, and Ruby are frequently utilized.
Don’t worry about all this coding, we have a perfect no-code website to app builder solution for you!
Swing2App no code website to app converter you can convert your pre-existing website to app in just 5 minutes!
To know more about top node app builders read our blog: No Code App Builders For 2022: What Is The Best No-Code App Builder?
Benefits of Web Apps
Web apps have many advantages, the main benefits of which are:
1.Cost-efficient
Lowering expenditure is the greatest advantage of web apps, especially small businesses and individuals. This is because they require less maintenance and may have fewer computing requirements (in terms of processing power and so on)
With Swing2App you can convert your website to app for both android and iOS devices at the same time! Confused about whether to make an Android or iOS app. Check out our blog: IOS Vs Android: Which Is Suitable For Your First App?
2. Easy to maintain
Web apps are easier to maintain than a desktop website since they use the same code across the application. There are no compatibility problems.
3. Multi-platform
Web applications may run on any platform, including Windows, Linux, and Mac, as long as recent browsers are installed. They provide mobile like features on website as well as mobiles, thus creating brand recognition. For example, Amazon.
4. App store and updates
In online apps, permission from the app store is not necessary.
Another advantage of adopting web apps is that updates are automatic, and because they’re deployed centrally, everyone should be using the same version.
5. Save space (storage efficiency)
Web applications are Internet-enabled apps that may be accessed using the web browser on a mobile device. As a result, there is no need to download or install them.
Subscription-based web apps, such as software as a service (SaaS), also aid in the reduction of online software piracy, which can cause significant issues. Because SaaS is only accessible via the cloud, consumers can only utilize it after paying for it. Because such programs may be accessed totally online, they do not require installation.
6. Enhanced user experience
You may improve your entire mobile UX by converting a website into an app.
Web Apps provide a direct path from a single touch, which may be initiated by a home screen icon or a push notification. The native navigation and functionality inside the app provide for a significantly smoother, slicker experience.
They have easier access to common device controls like swiping and pinching, which improves the user’s experience. Web Apps are just better designed for mobile devices and hence enhance user experience.
Web Application vs. other application types
We’ve previously mentioned that there are several sorts of applications. Although we’re primarily concerned with web apps, it’s worth pausing to consider other types, such as mobile and hybrid apps. We’ll give you a fast rundown of what they are, what functions they have, and a quick summary of their many benefits and drawbacks.
Web apps, mobile apps, and hybrid apps each offer their own set of benefits. As a result, it’s critical to examine the benefits and drawbacks of each before determining which is ideal for you. Each application has a distinct function.
Mobile apps
Mobile applications (also known as native apps) are particularly popular. Native apps are software programmes created specifically for a platform or device, such as Android or iOS. For that reason, they’re written in a specific programming language. Users often obtain them via app stores and install them directly on the devices in question.
Web apps are occasionally contrasted with native apps in the mobile computing industry, which are programs that are designed expressly for a platform or device and deployed on that platform or device. The two, however, are not mutually exclusive.

Native programs are those that are downloaded and built expressly for the device on which they are installed. On a mobile device, native apps may frequently take advantage of device-specific hardware, such as a GPS or camera.
Mobile applications may serve a wide range of purposes, from assisting us in finding routes to our desired locations to delivering multimedia material to our mobile devices.
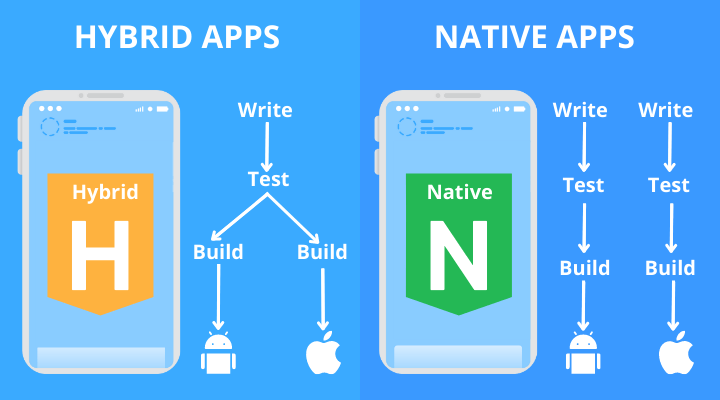
Hybrid apps
The Hybrid applications are programs that mix the two methodologies. These applications function similarly to Web apps, but they are installed on the device in the same way that native apps are. Internal APIs allow hybrid apps to take use of device-specific resources.
Hybrid apps do not have this capability; nonetheless, downloaded native programs can occasionally work offline. Because hybrid applications are built on Web apps, they will usually include comparable navigation components.
There are also hybrid applications, which include characteristics of both mobile and online apps, as the name implies. On the surface, hybrid apps appear to be identical to native apps. They’re made with Ruby, JavaScript, HTML5, and Cascading Style Sheets, among other computer languages (CSS).
Hybrid applications are installed on a mobile device in the same way that native apps are, and they appear to the end-user to be the same. Internally, though, they are just web applications with a frontend dashboard.
Advantages and drawbacks
Both native and hybrid apps offer advantages. Offline functionality is available in both mobile and hybrid applications (despite the latter’s underlying resemblance to web apps). They can also use the resources of the device on which they’re installed.
This implies they’ll be able to employ features like cameras and GPS. Web applications, on the other hand, must be accessible through a web browser; as a result, web apps cannot be used when users are offline.
When compared to online applications, however, there are several drawbacks. To begin, mobile and native applications must be obtained from an app store and installed. They must be installed on the smartphone, which means they consume storage space, which can quickly run out, causing users to shuffle their current programs to find places for new ones. Web browser plugins may be available for mobile apps.
There’s also the problem of upgrades to consider. Users of mobile and hybrid applications may be required to download updates manually, which implies that various versions of the same software may be used by different people, making team cooperation more difficult.
Web applications, on the other hand, are automatically updated from a central location. Users are not forced to perform any tasks, which saves them time and allows for more effective communication.
Conclusion
A hybrid app is a good choice if you’re searching for a low-cost bespoke app development alternative. Swing2App, a website to app converter and no-code app developer, offers a variety of mobile app services to assist your company in growing.
We’ve also turned several websites into mobile applications for clients all around the world. As a result, we can better understand your business and design the finest app possible while keeping your budget and deadline in mind.
